Key Insights
- RipperSec is a pro-Palestinian, pro-Muslim hacktivist group operating from Malaysia.
- RipperSec has been operating on Telegram since June 2023 and has accumulated over 2,000 members in a little over a year.
- MegaMedusa is a publicly available Web DDoS attack tool created and maintained by a member of the RipperSec group.
- MegaMedusa can be installed in just five simple commands, allowing anyone to launch highly scalable Web DDoS attacks against targets of their choice.
- The MegaMedusa attack tool uses ten randomisation techniques to diversify its attack requests and make the detection and mitigation of its attacks harder.
- MegaMedusa makes some rudimentary attempts to evade CAPTCHA triggers through randomisation and proxy use, but it does not include advanced CAPTCHA-solving capabilities.
- RipperSec’s threat and scale do not come from a large and sophisticated attack infrastructure but from its community. The community has always been activists’ and hacktivists’ most potent weapon.
RipperSec, a pro-Palestinian and pro-Muslim hacktivist group based in Malaysia, has been active on Telegram since June 2023, amassing over 2,000 members in just over a year.
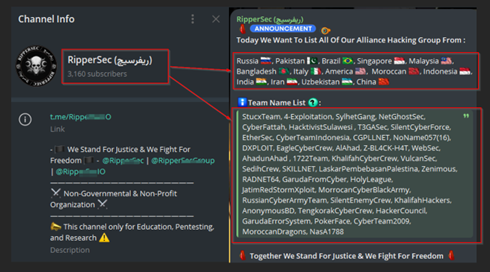
Recently, RipperSec announced the formation of a powerful global hacking alliance, uniting a diverse range of hacking groups from 14 countries worldwide.
RipperSec’s global hacking alliance is characterised by its international scope and the diversity of its member groups. This alliance spans continents and includes both well-known and lesser-known hacking groups. The alliance’s broad geographic distribution and varied expertise highlight its potential to execute complex, multi-layered cyber operations.
Well-known RipperSec allies and their capabilities
- StucxTeam (Russia): Known for high-profile ransomware attacks and advanced exploitation techniques. This group has been involved in several significant breaches and is recognised for its technical sophistication and operational secrecy.
- NoName057(16) (Russia): This group specialises in targeted attacks against high-value targets, including government and corporate entities. They are known for their stealthy tactics and advanced malware.
- CyberFattah (Iran): Associated with cyber espionage and attacks on critical infrastructure. This group operates with geopolitical motives, often targeting entities linked to regional and global conflicts.
- HacktivistSulawesi (Indonesia): Focuses on politically motivated cyber-attacks. They often target organisations perceived as engaging in activities contrary to their political or social agendas.
- EagleCyberCrew (Morocco): Engages in financial cybercrime, including fraud and data theft. This group uses a combination of phishing and sophisticated malware to compromise financial institutions.
- Zenimous (India): Known for their involvement in various cybercriminal activities, including data theft and financial fraud. Their tactics often involve exploiting vulnerabilities in economic systems.
TA profile specialisations and their techniques
- Ransomware: Groups like StucxTeam and NoName057(16) are prominent in deploying ransomware, which can weaken organisations by encrypting critical data and demanding ransom.
- Cyber Espionage: Iranian groups like CyberFattah are known for their espionage activities, aiming to extract sensitive information from governmental and corporate entities.
- Hacktivism: Indonesian groups such as HacktivistSulawesi use their cyber capabilities to promote political causes and disrupt organisations they view as adversaries.
- Financial Cybercrime: Moroccan groups like EagleCyberCrew and Indian groups like Zenimous focus on financial crimes, targeting banks and financial institutions for data theft and fraud.
Countries and hacking groups involved
|
Country |
Hacking Groups |
| Russia | StucxTeam, NoName057(16), VulcanSec, RussianCyberArmyTeam, SilentEnemyCrew |
| Pakistan | 4-Exploitation, AlAhad, KhalifahCyberCrew, AhadunAhad, HackerCouncil, CyberTeam2009 |
| Brazil | EtherSec |
| Singapore | NetGhostSec |
| Malaysia | HacktivistSulawesi, SKILLNET |
| Bangladesh | SylhetGang, LaskarPembebasanPalestina, AnonymousBD |
| Italy | SilentCyberForce |
| America | Potential connections, indirect involvement |
| Morocco | EagleCyberCrew, WebSec, HolyLeague, MoroccanCyberBlackArmy, MoroccanDragons |
| Indonesia | CyberTeamIndonesia, GarudaFromCyber, SedihCrew, JatimRedStormXploit, TengkorakCyberCrew, GarudaErrorSystem |
| India | CGPLLNET, Zenimous, PokerFace |
| Iran | CyberFattah, 1722Team |
| Uzbekistan | DXPLOIT |
| China | Z-BL4CK-H4T, RADNET64 |
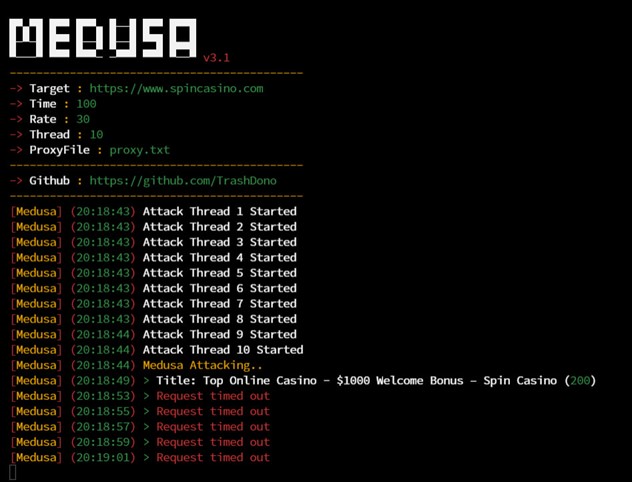
MegaMedusa: DDoS attack kit developed & maintained by RipperSec
MegaMedusa is a potent Web Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack tool developed and maintained by a member of the RipperSec group. Designed to perform Layer 7 (application layer) DDoS attacks, MegaMedusa is accessible and versatile thanks to its public availability and open-source code.
MegaMedusa is a publicly available Web DDoS attack tool created and maintained by a member of the RipperSec group.
Technical specifications
- Language and Environment: MegaMedusa is written in JavaScript and operates as a command-line tool within the Node.js runtime environment. Node.js is favoured for its asynchronous and non-blocking I/O capabilities, which enable it to handle numerous network connections simultaneously and efficiently. This characteristic is particularly advantageous for executing DDoS attacks that require managing a high volume of requests.
- Cross-Platform Functionality: One of the key benefits of using Node.js is its cross-platform compatibility. MegaMedusa can run on multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux, without needing modifications for each platform. This flexibility makes it accessible to a wide range of users.
- Source Code: The source code for MegaMedusa is publicly available on GitHub. Although the JavaScript code is obfuscated, it can be deobfuscated to recover the readable code. This transparency allows users to study and understand the tool’s inner workings and modify or improve it.
Usage and impact
- Layer 7 DDoS Attacks: MegaMedusa targets the application layer, a crucial aspect of web services. By overwhelming a web server with a flood of requests, the tool can cause significant disruptions, making websites and online services inaccessible to legitimate users.
- Efficiency: Leveraging Node.js’s asynchronous I/O model, MegaMedusa efficiently manages multiple connections and requests. This capability enhances its effectiveness in executing large-scale attacks and maintaining performance under high-traffic conditions.
RipperSec presence on another platform
Apart from an active presence on Telegram, RipperSec also has an alternative presence on other social media/online platforms.
- VX Account: The account was recently created on August 29th. RipperSec shared multiple posts with evidence containing DDoS proofs, CCTV accesses, defacement, and more.
- Username: @rippersec
- Twitter Account: The account has been active since February 2016. So far, there has been no significant activity on their Twitter account.
- Username: @RipperSec
Conclusion
The revelation of RipperSec’s global hacking alliance underscores the evolving nature of cyber threats and the need for robust and adaptive defence strategies. With a diverse range of groups and capabilities, this alliance presents a complex challenge for global cyber security. By enhancing defences, fostering international cooperation, and staying informed about emerging threats, organisations and governments can better prepare to address and mitigate the risks posed by this expansive and sophisticated threat network.