iZOOlogic Red Team researchers recently discovered a highly advanced spear phishing campaign targeting users through the dynamic alteration of website UI based on email addresses embedded in URLs.
How It Works
This alarming tactic unfolds in three distinct stages:
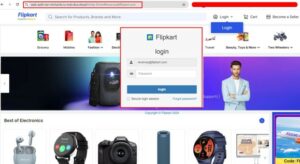
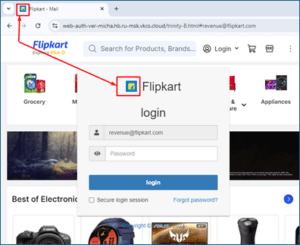
- Dynamic UI Manipulation: The attack begins with URLs containing an email ID, such as #revenue@xyzcompany.com. A sophisticated script embedded on the website extracts the domain from this email ID and displays it within an iframe on the webpage, creating a convincing front that mimics a legitimate site.
- Brand Targeting: By incorporating an employee’s email address into the URL, attackers can dynamically tailor the phishing page to target any brand. This method leverages the appearance of authenticity, making the phishing attempt more believable to the victim.
- Data Exfiltration: Once the user submits their credentials on the counterfeit site, this information is promptly sent to the attackers’ Telegram account (@controlroom1717). Telegram serves as the Command and Control (C2) server, facilitating the collection and management of stolen data.
Technical Findings
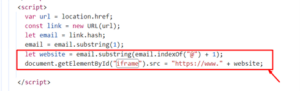
- Dynamic Domain Tracking: The JavaScript code snippet embedded in the source code is responsible for tracking the email domain mentioned in the URL. The extracted domain is further parsed to embed any legitimate website into the iframe element.
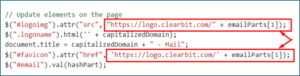
- Loading Target Domain Logo & Favicon: The following code snippet is used to load the target email domain’s logo and favicon via a third-party service, “clearbit[.]com.”
- Credential Compilation: When a victim inputs their credentials on the fraudulent site, the collected information—including the user’s email, password, browser details, and the current date—is systematically compiled and stored. This meticulous compilation helps in organising and managing the stolen data.
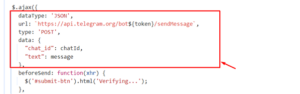
- Exfiltration via Telegram Bot: The stolen credentials are sent to a Telegram bot through another code snippet. The bot then forwards this sensitive information to a designated Telegram user account, facilitating efficient data exfiltration and control.
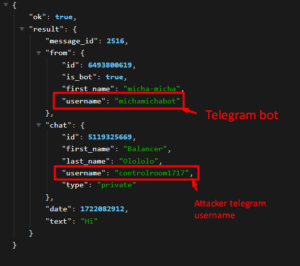
- Snapshots: Snapshots of the Telegram bot and the attacker’s Telegram user account, where the compromised credentials are ultimately sent, are provided below for reference. These images illustrate the final stages of the credential theft process.
Indicator of Compromise (IOCs)
| Indicator | Type | Remarks |
| http[:]//web-auth-ver-micha[].hb[.]ru-msk[.]vkcs[.]cloud/trinity-B[.]html | URL | The attacker used cloud hosting platform “cloud[.]vk[.]com” to host the scam site. |
| 95.163.53.117 | IP | Attackers IP Address |
| @controlroom1717 | Telegram username | The attacker telegram user account. |
| @michamichabot | Telegram bot | The telegram bot used to sent victim credential to the attacker telegram user account. |
Why This Is Concerning
The ability to dynamically personalise phishing pages based on email addresses makes these spear phishing campaigns more convincing and increases the likelihood of users falling victim to the scam. The discovery of this spear phishing campaign highlights the evolving sophistication of cyber threats. The use of dynamic website UI alterations based on email addresses embedded in URLs represents a significant advancement in phishing tactics.
To stay safe, iZOOlogic security researchers advise to be vigilant about URLs, especially those with suspicious patterns. Always verify unexpected or unusual emails, ensure your cybersecurity defences are up-to-date, and share this information to help protect our community from these sophisticated phishing tactics.

Nice work from Pankaj